Overview
Ledgera is a decentralized and distributed infrastructure designed to ensure the availability of data and the integrity of computation results.
A system running Ledgera operates across a network of computer nodes that may play distinct roles so as to provide the following features :
- Reliable long-term storage of data
- Byzantine-Fault-Tolerant execution of distributed computations
- Providing Proofs of data availability
- Providing Proofs of integrity for the results of computations
Ledgera components
The atomic behavioral entity in Ledgera is a “component”. We distinguish between 5 types of components:
| Icon | Description |
|---|---|
 | User Application: An external system or application that interacts with Ledgera by defining and submitting computation requests, storage requests or argument proposals. |
 | Ledgera Client: The gateway component that interfaces with the user application. It formats, signs, and sends computation requests, storage requests or argument proposals to the Ledgera network and handles the returned results and proofs. |
 | Computation and Verification Component: Votes on granting write access to storage, executes computations locally and vote on the result integrity, produces proofs of storage and of the integrity of computation results. |
 | Storage Component: Maintains a persistent replicated storage of data which guarantees that if a proof of storage exists, then the corresponding data is available in at least one honest storage component. This component is optional and can be enabled depending on the application’s needs. |
 | Secure Log Component: Maintains an append-only auditable log of events which allows for audit and enable agreement on concrete values for unknown arguments of computations. This component is optional and can be enabled depending on the application’s needs. |
Ledgera nodes and their roles
A ledgera network consists of a number of ledgera nodes on which Client, Computation, Storage and Log components are deployed. We have at most one component of each kind running on a single ledgera node. Whenever a certain component is deployed on a ledgera node, we may say that it plays the corresponding role.
In the example network below, we have 4 ledgera nodes such that :
- Left node plays the Client and Computation roles
- Top node plays the Storage and Computation roles
- Bottom node plays the Secure Log role
- Right node plays the Client, Computation and Storage roles
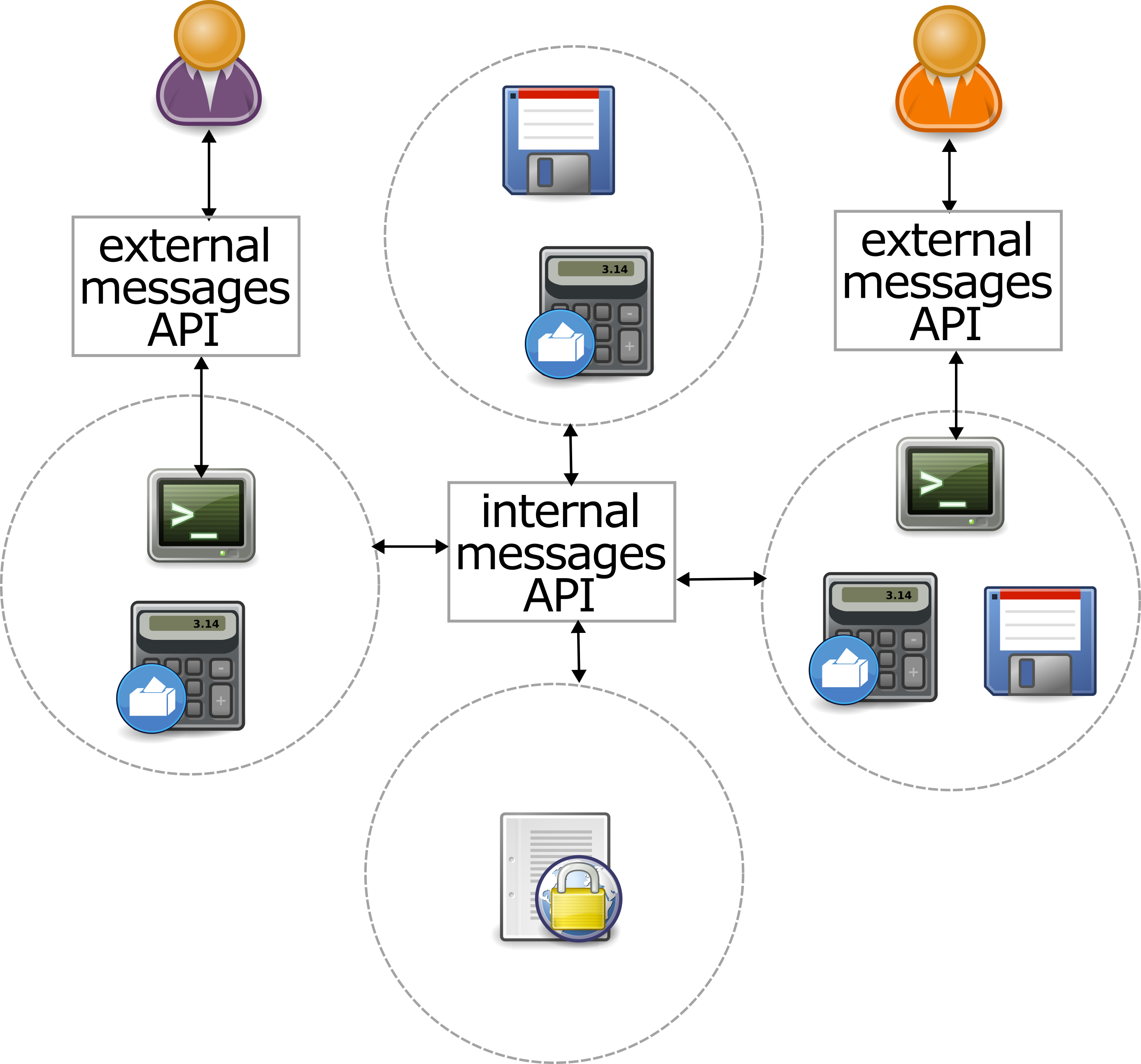
Users exclusively communicate with Client components, via a dedicated “external messages API” which allows sending requests to the system and retrieving information.
Ledgera nodes communicate among themselves via a dedicated “internal messages API” to implement the features of Ledgera.
Foundational Design Properties
Existing :
- Modularity and Deployment Flexibility: Ledgera’s architecture is designed to allow seamless modularization, giving users flexibility in deploying components as needed.
- Byzantine Fault Tolerance: Ensures resilience against malicious actors or system failures, maintaining reliability even in the presence of a bounded fraction of attackers.
- Unlike blockchain, which is limited to smart contract or DApp execution, Ledgera enables complex, customizable computations.
- Native Support for Secure Storage and Computation: Ledgera natively integrates secure storage mechanisms and computation protocols, ensuring both the confidentiality and integrity of sensitive data and computations. This design allows users to perform operations with guaranteed security, without the need for additional layers or external tools.
- Native Support for Auditability: Storage and computations respectively yield proofs of storage and of integrity, which are appended to the log, allowing transparent tracking and verification of data and computations in the system.
- State Machine Replication only on demand. Ledgera does not require consensus to be executed for every computation. It only does so if an agreement is required on input arguments (in cases where one or several of its arguments are unknowns).
Planned :
- Native Support for Non-Determinism: Ledgera supports non-deterministic computations, enabling greater flexibility in executing various use cases as Trustworthy Federated Learning.
- Ledger-Agnostic: The Ledgera secure log can be seamlessly integrated with any underlying ledger technology, allowing it to be used in a wide range of scenarios and applications without being tied to a specific blockchain.